Cash flows or the assets of the company being acquired usually secure the loan. Mezzanine debt is a private loan, usually provided by a commercial bank or a mezzanine venture capital firm. Mezzanine transactions often involve a mix of debt and equity in a subordinated loan or warrants, common stock, or preferred stock. Equity is used as capital raised by a company, which is then used to purchase assets, invest in projects, and fund operations. A firm typically can raise capital by issuing debt (in the form of a loan or via bonds) or equity (by selling stock).
- It is also the most heavily relied on approach, as it incorporates all aspects of a business and is, therefore, considered the most accurate and complete measure.
- Finally, Lion records the net income from Zombie as an increase to its Investment account.
- When calculating equity in accounting, the company’s assets are offset by its liabilities.
- If the business owes $10,000 to the bank and also has $5,000 in credit card debt, its total liabilities would be $15,000.
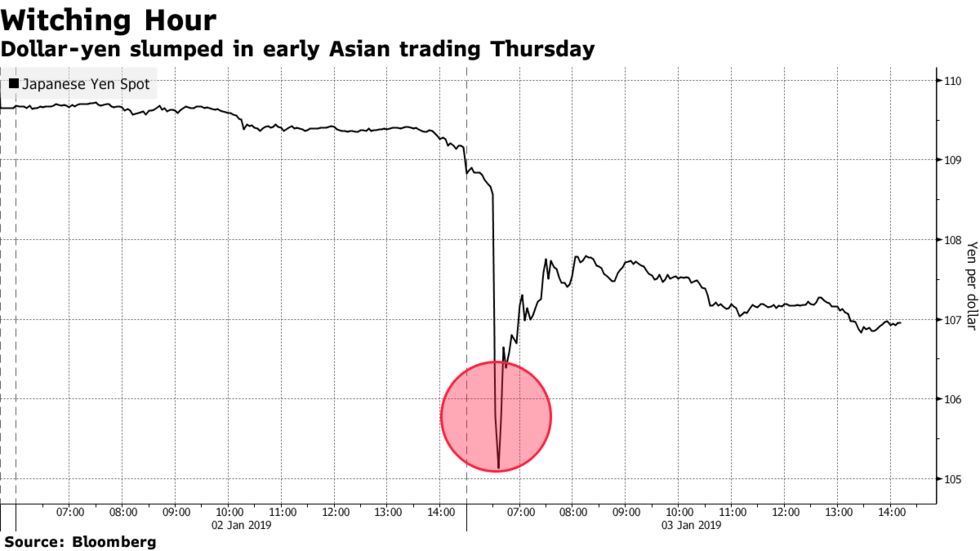
ROE is a financial metric that measures how much profit is generated from a company’s shareholder equity. When an investment is publicly traded, the market value of equity is readily available by looking at the company’s share price and its market capitalization. For private entities, the market mechanism does not exist, so other valuation forms must be done to estimate value. It’s the difference between your personal assets (like your home, savings, or retirement accounts) and your personal liabilities (like credit card debt or a mortgage). Others were more bullish about the impact of this year’s the turmoil would have on the chance to attract private equity back to banks. The Great Recession was the last significant liquidity crunch that the banking sector faced, which increased the number of private equity investors committing capital to shore up faltering and distressed banks.
Types of Private Equity Financing
Nevertheless, the owners and private shareholders in such a company can still compute the firm’s equity position using the same formula and method as with a public one. The profit and loss statement (also called the income statement) summarizes the revenues and expenses of a company over some time. The balance sheet illustrates a company’s financial position at a certain point in time.
These shares that are purchased by the company are called treasury stock. This formula is a fundamental equation in accounting and provides a snapshot of a company’s financial health. It’s important to note that positive equity indicates that the company has more assets than liabilities, which is generally a good sign for investors and creditors. Shareholders’ equity (stockholders’ equity) is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. It represents the net value of a company and is a critical component of its balance sheet. A company’s book value is the difference between the total assets and total liabilities.
Equity Accounts
If your equity number is negative, it means your liabilities outweigh your assets. For an individual, equity refers to the ownership interest in an asset. For example, a person owns a home with a market value of $500,000 and owes $200,000 on the related mortgage, leaving $300,000 of equity in the home. Total equity effectively represents how much a company would have left over in assets if the company went out of business immediately. A company’s equity position can be found on its balance sheet, where there is an entry line for total equity on the right side of the table. Other sources define equity differently, but they all refer to the same thing.

For instance, if someone owns a $400,000 home with a $150,000 mortgage on it, then the homeowner has $250,000 in equity in the property. Still, Burgess added that he’s “more negative” about the potential resurgence of bank M&A due to stock-price valuations, rising interest rates, the potential for a recession and regulatory approval of deals. Because of that, from an accounting perspective, Banc of California’s balance sheet was used as if the bank was the seller, though in practice, the Santa Ana institution is buying PacWest’s operations. Unlike with the consolidation method, in using the equity method there is no consolidation and elimination process. Instead, the investor will report its proportionate share of the investee’s equity as an investment (at cost).
The book value of equity
When liabilities attached to an asset exceed its value, the difference is called a deficit and the asset is informally said to be “underwater” or “upside-down”. In government finance or other non-profit settings, equity is known as “net position” or “net assets”. When an investor exercises full control over the company it invests in, the investing company may be known as a parent company to the investee. In such a case, investments made by the parent company in the subsidiary are accounted for using the consolidation method. Lion receives dividends of $15,000, which is 30% of $50,000 and records a reduction in their investment account.
The preferred stock is a type of share that often has no voting rights, but is guaranteed a cumulative dividend. If the dividend is not paid in one year, then it will accumulate until paid off. Accountants use this equity value as the basis for preparing balance sheets and other financial statements.
How to Calculate a Company’s Equity FAQS
The other meaning equity has in accounting refers to its market value, meaning how much it’s worth to investors. This equity value is based on current share prices (how much a share of your company costs) or determined by the investors themselves. Also called ‘shareholders’ equity’ or ‘net worth’, it represents the total value of all your company’s assets after you’ve paid your liabilities. For businesses, what counts as equity in accounting is recorded on the company’s balance sheet.
Carlyle reports lower than expected 26% slump in Q2 earnings – Reuters
Carlyle reports lower than expected 26% slump in Q2 earnings.
Posted: Wed, 02 Aug 2023 10:05:00 GMT [source]
The value of common stock is equal to the par value of the shares times the number of shares outstanding. For example, 1 million shares with $1 of par value would result in $1 million of common share capital on the balance sheet. The meaning of equity in accounting could also refer to an individual’s personal equity, or net worth. As with a company, an individual can assess his or her own personal equity by subtracting the total value of liabilities from the total value of assets. Personal assets will include things like cash, investments, property, and vehicles. Personal liabilities tend to include things like lines of credit, existing debts, outstanding bills and mortgages.
Owning equity will also give shareholders the right to vote on corporate actions and elections for the board of directors. These equity ownership benefits promote shareholders’ ongoing interest in the company. You simply take every asset listed on your company’s balance sheet and subtract total liabilities to find the book value. Equity in accounting comes from subtracting liabilities from a company’s assets. Those assets can include tangible assets the company owns (assets in physical form) and intangible assets (those you can’t actually touch, but are valuable).
- The term “equity” can be used in a number of different ways, from home value to investments.
- Mark-to-market is an accounting method that measures a company’s assets and liabilities at their current market value.
- Owner’s equity is typically seen with sole proprietorships, but can also be known as stockholder’s equity or shareholder’s equity if your business structure is a corporation.
- In exchange for money, the business gives up some of its ownership, typically a percentage of shares.
- The concept of equity applies to individual people as much as it does to businesses.
In other words, when a company gives shares, the value of all issued shares gets added to the company’s capital. At some point, the amount of accumulated retained earnings can exceed the amount of equity capital contributed by stockholders. Retained earnings are usually the largest component of stockholders’ equity for companies operating for many years.
Equity Template
Similar to the cost method, equity accounting records the investment as a cost. The investment is subsequently adjusted to account for the investor’s share of the company’s profit and loss. For instance, a company, ABC, acquires a 45% stake in another company, DEF, for $25 million. This $25 million investment in DEF earns ABC a seat on the board of directors. If, at the end of an accounting period, the DEF records $6 million income, ABC would get 45% of that income amount. The amounts for liabilities and assets can be found within your equity accounts on a balance sheet—liabilities and owner’s equity are usually found on the right side, and assets are found on the left side.

Receive timely updates on accounting and financial reporting topics from KPMG. Learn what owner’s equity is, how it affects you and your business, how to calculate it, as well as helpful examples. As a business owner, you can usually only afford to invest a certain amount of your own money in your business. For small businesses and sole traders, knowing your equity enables you to determine where you can do better to help grow your business.
Equity financing can give aspiring business owners the capital needed to realize their dreams. This means they might have to give the other investors free adp direct deposit authorization form a say in decisions about how to run the business. You may already be familiar with the term equity as it applies to personal finances.
This account also holds different types of gains and losses resulting in the sale of shares or other complex financial instruments. Accountants take all these pieces of the puzzle to track a company’s value. They must also include any share capital and retained earnings in the equation. Shareholders’ equity is an essential metric to consider when determining the return being generated versus the total amount invested by equity investors. Market analysts and investors prefer a balance between the amount of retained earnings that a company pays out to investors in the form of dividends and the amount retained to reinvest back into the company.